Green Energy Handbook – Part six: The main tasks of data management
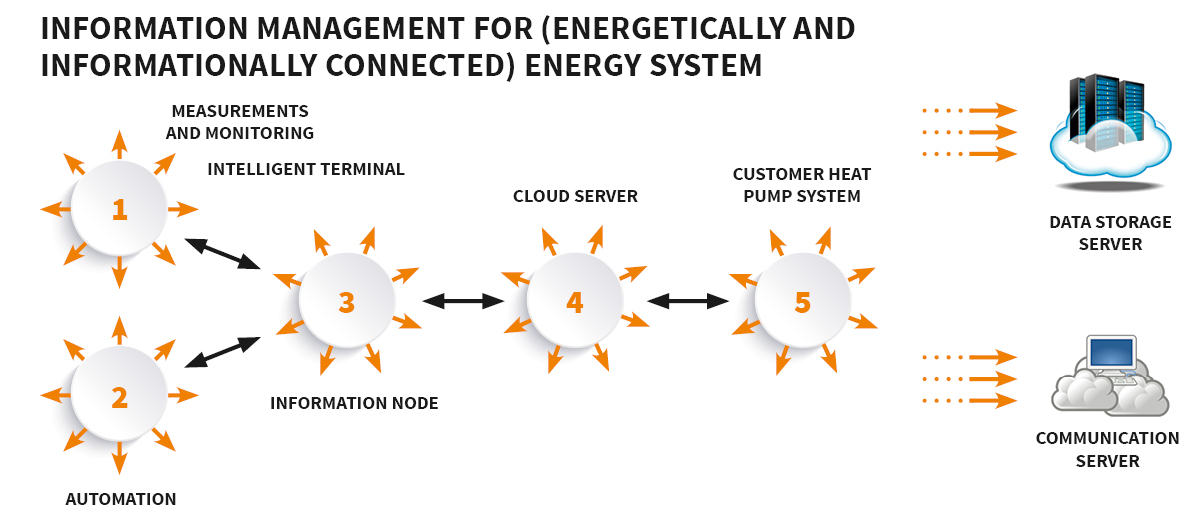
Provide fast, real-time information and communication for local handlers and operators – for example via a smart terminal.
It is possible to pre-program the thermal condition of a building, for example for events.
Under extreme temperature conditions, the connected energy system allows the available energy to be reallocated – for example, in extreme cold, it is possible to increase the heating while reducing the air exchange as much as possible.
Ensuring fast and remote access to information – for example for system monitoring or to monitor and evaluate the economics of operation.
One of the basic issues of energy financing is to have reliable data on consumption and savings available to the financier at all times.
Remote access to the information allows the energy service provider and maintenance to perform remote intervention – for example for optimization and / or to set the emergency operating state in the event of a failure.
The information can be made available, for example, to a resource management company or a security company.
Establishing a database connection – for example in BIG DATA or an ERP program (for example: SAP).
Creating BIG DATA and building a data connection to it is valuable if you want to perform further optimization using smart algorithms.
By connecting to the ERP program, the financial data can be transferred to the system program immediately, so energy management can be integrated online into, for example, company management.
Establish effective information security.